Botulism
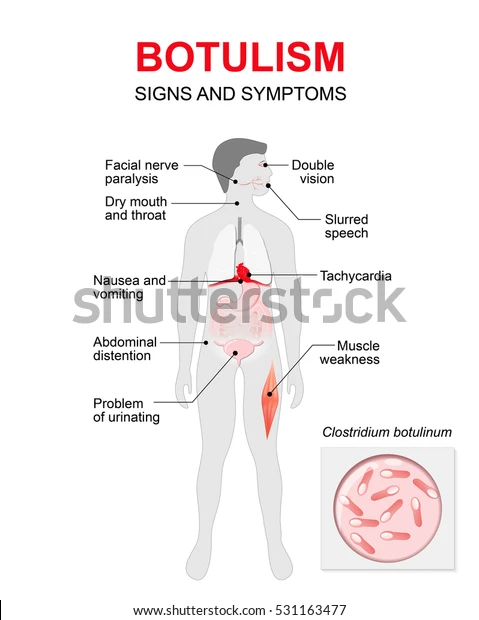
Toxins that cause skeletal muscular paralysis cause botulism, a rare but dangerous sickness. Muscles that help you breathe and move are affected by this paralysis.
What is Botulism?

Botulism is a life-threatening disease that attacks the nervous system. Botulinum toxins, which are harmful chemicals, cause skeletal muscular paralysis. The muscles that help you move and breathe may be affected by this paralysis.
It is a rare disease. People with symptoms of botulism should contact a doctor as soon as possible because it can be fatal.
What are the types of botulism?
Botulism can come in a variety of forms. The most prevalent types are:
Food borne botulism
When people ingest tainted foods that already contain the toxin, they get foodborne botulism.
The meal that has been improperly processed may allow bacteria to proliferate, which subsequently releases the poison into the food. Foodborne botulism is commonly transmitted through home-canned or inadequately canned store-bought foods. Other foods that have been linked to this condition include:
- Oils that have been infused with herbs
- Baked potatoes in aluminum foil
- Sauces with cheese
- Garlic in a bottle
- Foods that have been kept heated or unrefrigerated for an extended period of time
Infant botulism
Infant botulism is caused by babies ingesting bacterial spores found in soil or being fed foods containing the spores, the most common of which being honey. The spores then turn into bacteria, which multiply inside the baby’s intestines and emit poison.
Natural defenses against colonization exist in older children and adults, but not in infants under the age of 12 months. As a result, experts recommend that babies wait until they are at least one year old before eating honey.
Wound botulism
When the clostridium bacteria enters into a wound and multiplies, it causes wound botulism. This type of botulism is more common in those who inject drugs into their veins using a needle. It can also arise after surgery or a catastrophic injury in rare situations.
What is the prevalence of botulism?
Each year, just a few cases of botulism are documented in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) received 205 confirmed cases in 2016.
SYMPTOMS AND CAUSES
What causes botulism?
Botulinum toxins are produced by bacteria such as Clostridium botulinum and Clostridium butyricum. These bacteria spores are often found in soil, although they rarely cause illness in humans.
Bacterial spores can germinate and proliferate under certain conditions. The poison is then secreted by the adult bacterium. When the poison is released, it spreads quickly through the circulation and binds to nerves. When those nerves stop working, botulism develops. The following conditions allow spores to germinate:
- Lack of oxygen
- Low acidity, sugar or salt
- Cooking temperatures that are too low (even boiling may not destroy the spores)
- Storage temperatures that are too warm
What are the symptoms of botulism?
Botulism commonly manifests itself in the muscles of the face, eyes, and throat. Symptoms might extend to other sections of the body if not treated. After eating botulinum spores, symptoms might occur anywhere from a few hours to many days later. Among the signs and symptoms are:
- Drooping eyelids
- Double or blurred vision
- Slurred speech
- Dry mouth
- Trouble swallowing
- Difficulty breathing
- Weakness or paralysis of arms or legs
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTS
How is diagnosed?
Doctors do a physical examination to diagnose botulism. They look for muscles that are weak or paralyzed. Other illnesses that cause similar symptoms include stroke and Guillain-Barre syndrome. Doctors may need to conduct additional testing to confirm that it is botulism.
Your doctor can run a test to see if the toxin is present in your blood, stool, or vomit to confirm the diagnosis. Food samples suspected of containing the toxin can also be examined. Nerve conduction investigations are another test (EMG). Because the findings of these tests can take several days to arrive, doctors frequently begin treatment before the results are received.
MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT
How is treated?
To remove botulinum toxins from the body, doctors utilize a number of treatments. The most common treatment is antitoxin, which is given by a doctor. Antibodies in this drug attach to and neutralize the poison, halting the toxin’s effects on the body.
Wound botulism patients may require a procedure in which the contaminated component of the wound is surgically removed. People are given antibiotics after the operation to prevent the infection from returning.
Botulism symptoms may necessitate therapy for certain people. They may need to use a ventilator (a breathing machine) until the paralysis that is preventing them from breathing subsides.
What are the complications or side effects of botulism?
The muscles that let you swallow and breathe can be paralyzed by botulism. It can induce respiratory difficulties, which can lead to death. It can also cause choking, which can result in the aspiration of food or mucus from your mouth.
What might people expect after botulism treatment?
Its recovery might take weeks, months, or even years, depending on the severity of the case. The majority of persons who receive immediate therapy recover in less than two weeks.
After surviving, some people experience fatigue and shortness of breath for years. They can manage their symptoms with breathing exercises and other therapy. People who have persistent respiratory issues may need to use a ventilator for weeks or months.
PREVENTION
Can be prevented?
Yes, there are things you may take to help prevent the most prevalent forms of botulism.
Foodborne botulism:
- Food should refrigerate within 2 hours of cooking. The bacteria cannot produce spores if they are kept cool.
- Make sure the food is completely cooked.
- Food containers that appear to be damaged or bulging should be avoided. (These could be indicators of bacteria producing gas.)
Infant :
Honey should not be given to children under the age of one year.
Wound :
- Injectable medications should not be abused.
- If a wound shows signs of infection, such as redness, soreness, swelling, or pus, seek medical attention.
- Thoroughly clean wounds that have been polluted by dirt and soil.
OUTLOOK / PROGNOSIS
What is the prognosis for botulism patients?
If left untreated can be lethal. However, the majority of persons who receive quick diagnoses and treatment can recover completely from their illness. Throughout their lives, they recover to normal function.



